Google Shopping for Business Owners: Your Secret Strategy to Maximize Sales

In the fast‑paced world of digital commerce, standing out is harder than ever. But what if there were a “secret weapon” you could deploy today to give your products prime visibility and accelerate sales? Google Shopping offers exactly that — when used smartly, it becomes a powerful lever to boost your revenue, outpace competition, and reach high‑intent buyers.
In this blog, we’ll dive into:
- What Google Shopping is (and how it works)
- Why business owners should care
- Key benefits (visibility, conversion, cost control)
- Step‑by‑step setup
- Optimization strategies & pitfalls
- Measuring success
- Real-world tips & use cases
- FAQs & conclusion
What Is Google Shopping (and How It Works)?
At its core, Google Shopping is a product listing service that lets retailers display their individual products directly in Google search results, the Shopping tab, image search, and other Google surfaces.
Unlike classic search ads (just text), Shopping listings show images, prices, titles, and merchant names. That makes them more visual, more informative, and more compelling to click.
Two core platforms power this:
- Google Merchant Center — where you upload your product feed (details about your products, images, prices, availability).
- Google Ads — where you set budgets, bidding strategies, and choose which products to promote.
When someone searches for a product query, Google’s algorithm matches relevant products from Merchant Center and displays them. If you’re running a Shopping campaign, your products can get top placement — and you pay only when someone clicks.
Note: Google also supports free product listings in many markets. That means even without paid ads, you can get your products into the Shopping tab — though ad placement gives you priority.
Why Business Owners Should Use Google Shopping
If you’re selling products (online or via hybrid models), Google Shopping offers unique advantages. Think of it as putting your products in front of shoppers at the moment they intend to buy. Here are several compelling reasons:
1. High Visibility at the Buyer’s Moment of Intent
People searching on Google with product keywords are already in a purchasing mindset. Seeing your product with image + price + review gives them immediate clarity — and reduces friction.
Your products get prime real estate — often above organic listings — which gives you a competitive edge.
2. Better Conversion Rates
Because users see product images, price, and merchant before clicking, you tend to attract more qualified traffic — people who are closer to buying.
Many case studies report higher conversion rates compared to standard search ads.
3. Cost Efficiency & ROI Control
You only pay when someone clicks (pay-per-click), meaning wasted impressions are less of a risk.
Because product ads are more granular (by item), you can allocate budget to your top performers. You also gain transparency into cost per click, cost per conversion, and ROI.
4. Scalable & Automated
Once your product feed is set, you can scale without micro-managing each ad. New items, inventory changes, and promotions can propagate automatically.
You can run broad campaigns or segment by product type, categories, margins, etc.
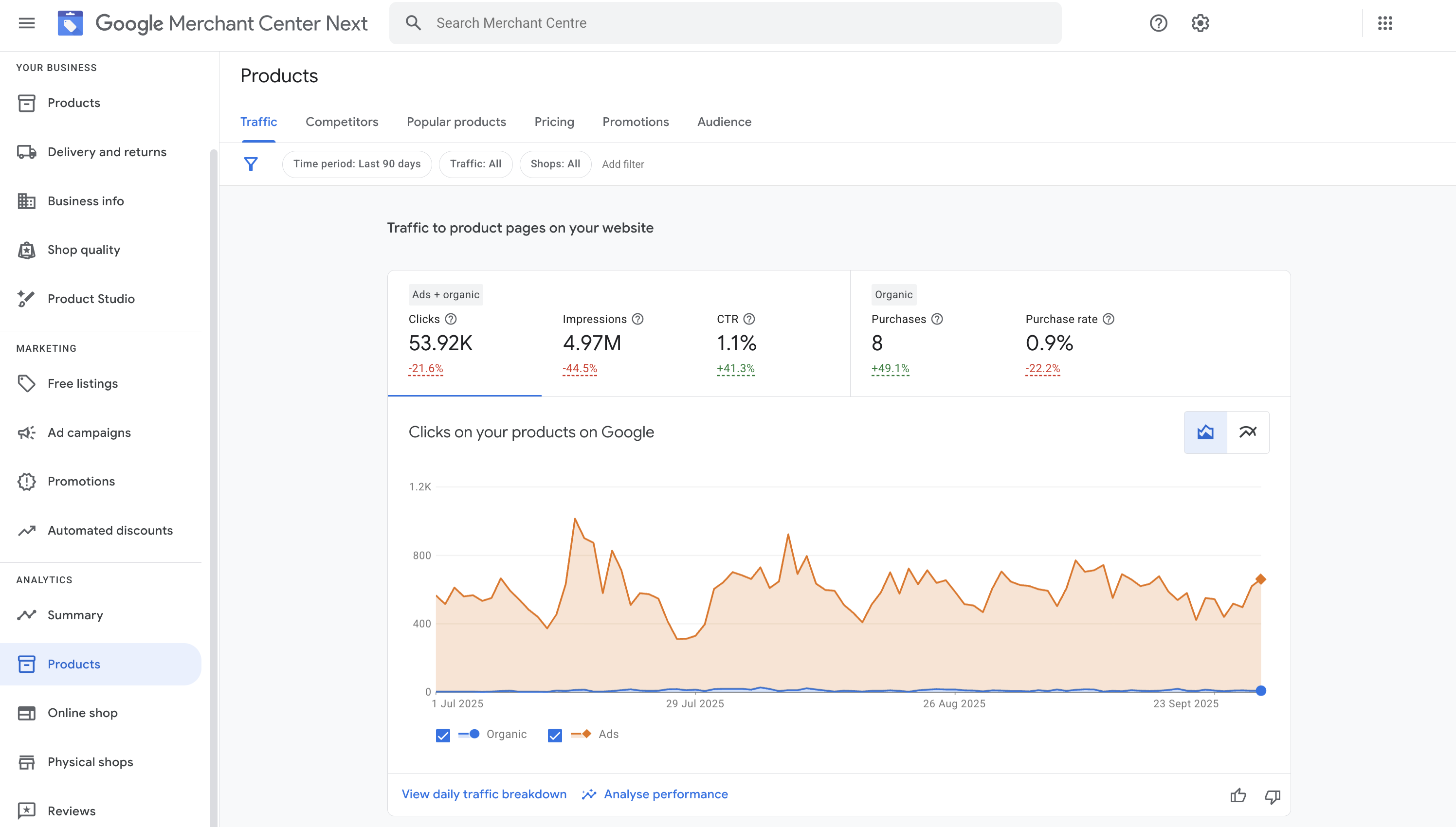
5. Rich Insights & Analytics
Merchant Center and Google Ads provide you with detailed analytics, including impressions, clicks, conversion metrics, search terms, and product performance.
These insights allow you to fine-tune your feed, pricing, bidding, and marketing strategy.
6. Omni‑Channel & Local Integration
If you have physical stores or local inventory, Google Shopping supports Local Inventory Ads, enabling nearby customers to view products available in their area.
Your products can also surface in Google Search, Google Images, YouTube, and Maps, amplifying reach.
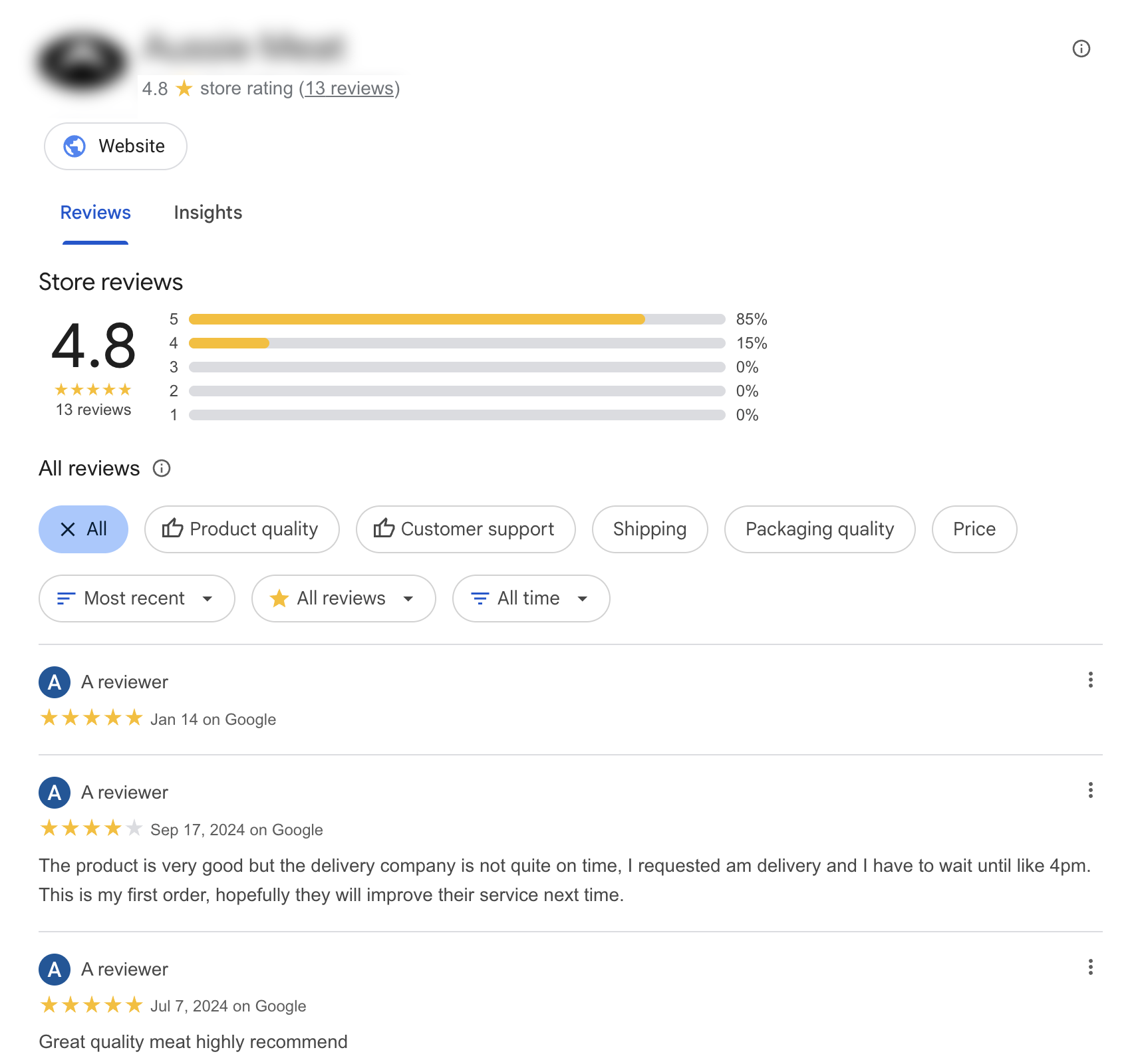
7. Brand Differentiation & Trust
Shopping ads allow you to show merchant branding, logos, ratings, and promotions, which helps differentiate you from competitors.
As consumers see your products with consistent data and reviews, it builds trust and credibility.
How to Get Started: Step-by-Step Guide
Let’s break down how to launch Google Shopping for your products.
| Step | Action | Tips / Notes |
| 1 | Set up a Google Merchant Center Account | Enter business details, verify your website, and complete any merchant policies. |
| 2 | Create & Upload Your Product Feed | Include required attributes: ID, title, description, price, availability, image link, etc. |
| 3 | Link to Google Ads / Enable Shopping Campaign | Connect Merchant Center with Google Ads. Choose “Shopping campaign” or Performance Max. |
| 4 | Set Your Budget & Bidding Strategy | Start modestly; you can always scale. Test manual vs automated bidding. |
| 5 | Segment Products / Prioritize | Group your bestsellers or high-margin items for more aggressive bids. |
| 6 | Optimize Titles & Descriptions | Use relevant keywords, avoid stuffing. Make them descriptive and clean. |
| 7 | Add High Quality Images | Clear background, good resolution, multiple angles, zoomable. |
| 8 | Implement Promotions / Discounts | Sales, promotions, “free shipping” tags attract clicks. |
| 9 | Monitor & Adjust | Use analytics daily/weekly: pause weak items, boost high performers. |
| 10 | Scale & Expand | Add more products, test new markets, and explore local inventory. |
Important checklist items:
- Make sure your product feed always stays up to date (price, stock)
- Comply with Google’s policies (no misleading data, correct landing pages)
- Use negative keywords to filter irrelevant search traffic
- Test different bidding approaches (manual vs smart)
- Use remarketing / audience signals to retarget interested visitors
Optimization Strategies (The Difference Between Okay & Exceptional)
Getting started is relatively straightforward, but optimizing is what drives real gains. Here are proven strategies:
1. Feed Quality Is King
Garbage in, garbage out. The better structured, clean, and consistent your product feed, the more Google trusts your listings — and the better your results.
- Use keywords in titles, but keep them legible
- Use full, descriptive attributes (brand, category, GTIN, MPN, color, etc.)
- Ensure images adhere to specs (no watermarks, good resolution)
- Handle variants (size, color) properly
2. Segment & Prioritize
Don’t treat your catalog as one block. Segment by performance, margin, or category. Bid higher on your bestsellers; be conservative on experimental items.
3. Bid Smarter
Test automated bidding (e.g. Maximize Conversion Value, ROAS targets) vs manual to see what suits your catalog and budget. Adjust bids by device, location, and time of day if you see patterns.
4. Use Negative Keywords / Exclusions
Even though Shopping campaigns operate differently from search, you can filter out irrelevant queries or poor-performing search terms to avoid wasted spend.
5. Leverage Promotions & Merchant Promotions
Adding special offers (discounts, “$X off,” free shipping) can boost click-through. Google often highlights promotional labels.
6. Test Titles & Descriptions
A small tweak in the title or description might shift click-through dramatically. Use A/B testing (e.g., reorder adjectives, remove filler words).
7. Optimize Landing Pages
Clicking product ads should land users directly on product pages optimized for conversion (fast load time, mobile responsive, clear “Buy” call-to-action).
8. Use Remarketing / Audience Signals
Integrate data signals (site visitors, cart abandoners) to improve targeting or to bid more aggressively toward warm audiences.
9. Leverage Local Inventory Ads (if applicable)
If you have physical stores and allow in-store pickup, Local Inventory Ads help drive foot traffic, combined with online conversions.
10. Seasonal & Promotional Tactics
Ahead of peak periods (e.g. holidays, festivals), increase bids, promote clearance or new items, and adjust budgets to capitalize on higher search volume.
Measuring Success: Key Metrics & KPIs
To know if Google Shopping is indeed your secret weapon, you need to measure diligently. Key metrics to track:
- Impressions / Clicks / CTR — How visible your products are and how appealing they are to click
- Conversion Rate — Percentage of clicks that lead to purchase
- Cost per Acquisition (CPA) — How much each sale costs you
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) — Revenue earned per ad dollar spent
- Average Order Value (AOV) — Higher AOV often justifies more aggressive bidding
- Product-level Performance — Some items may outperform others; focus on winners
- Search Queries / Search Terms — Understand what terms shoppers use
- Margins & Profitability — Don’t chase volume at the cost of margin
Set benchmarks and goals (e.g. target ROAS of x%, or CPA below a certain threshold). Adjust continuously.
Real World Examples & Use Cases
Spotlight Retail Group (multi-brand retailer) fixed feed gaps in Google Merchant Center and boosted SKU coverage by 231k, leading to a 30% increase in share of voice and a 10% rise in auction click share.
Local stores running Local Inventory Ads alongside Shopping see, on average, a 21% lift in store visits and a 9% lift in online conversions for products available in-store (Google data, July 2023–July 2024).
Officeworks used Performance Max for Store Goals (a Google Ads product that leverages Merchant Center product data) to drive offline sales, achieving a 10:1 incremental return and a 25% increase in store performance over four weeks.
Pitfalls & Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Poor feed data — missing images, incorrect prices, inconsistent attributes
- Overbidding on low-margin items — leads to negative ROI
- Neglecting landing page experience — slow speed, confusing layout, kills conversion
- Ignoring disapproved items — Google may disapprove listings for policy violations; fix immediately
- Not updating inventory & prices — mismatches cause disapproval or poor user experience
- Underutilizing negative filters — waste ad spend on irrelevant clicks
- Scaling too fast without control — monitor daily changes closely
Conclusion: Is Google Shopping Your Secret Weapon?
Yes — when approached strategically, Google Shopping can become your secret weapon to scale online sales, reach high‑intent customers, and outpace competition. Its visual format, strong buyer intent matching, cost control, and analytics make it one of the most powerful e‑commerce tools available.
But here’s the caveat: merely launching Shopping is not enough. It’s the continuous cycle of optimization — clean feed, smart segmentation, bid tuning, creative promotions, and data analysis — that transforms it from “a tool” into a revenue engine.
If you’re ready to take advantage, start small, test, learn, and scale aggressively. Over time, Google Shopping could power a significant portion of your digital sales — and become the secret weapon in your business growth arsenal.